Distal radius fracture types seen in the hand therapy clinic
Filed under Evaluation
Distal radius fractures are one of the most common injuries seen in hand therapy. Several different distal radius fracture classification systems have been developed, and this blog post will focus on the more common types of distal radius fractures and their classification.
Extra-articular fractures are either nondisplaced or displaced fractures. These fractures occur outside of the joint.
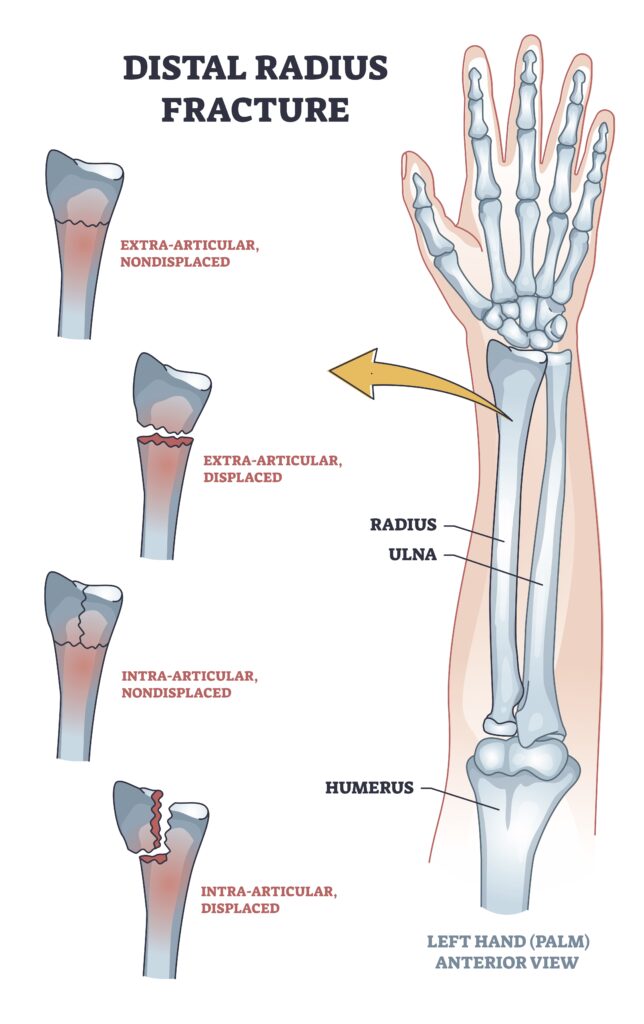
Similarly, Intra-articular fractures can be displaced or nondisplaced but occur within the joint.
Many fractures are named based on their fracture location, fracture pattern, and type of displacement.
Colles fractures are the most common type of distal radius fracture and account for about 90% of distal radius fractures. A Colles fracture is an extra-articular fracture with a dorsal displacement. These fractures occur from a fall forward on an outstretched hand.
A reverse Colles fracture is also known as Smith’s fracture. This is also an extra-articular fracture that is volarly displaced. These types of fractures are caused by falling backward and an outstretched arm.
Another type of distal radius fracture is a Barton’s fracture. This is an intra-articular fracture and is associated with a dislocation of the radio-carpal joint. A Barton’s fracture can be described as volar (more common) or dorsal (less common).
A die punch fracture is a depression fracture of the lunate fossa of the distal radius fracture that occurs with a vertical load through the lunate. These are often overlooked and not part of the classification system.
A Chauffeur’s fracture is also known as a radial styloid fracture or a Hutchinson’s fracture. This fracture is classified as an articular fracture. It was initially called a Chauffeur’s fracture because when the chauffeur would turn the crank to start the car, the motor often would cause the crank handle to jerk back.
1 Comment
Leave a Comment
More To Read
All about kinesiology taping for upper extremity injuries and conditions!
All about kinesiology taping! Elastic is also known as k-tape, Kinesio-tape, and kinesiology taping. Elastic tape is all over the marketplace and is often seen on professional athletes. It can be found in most therapy clinics and is used to treat both orthopedic and neurological conditions. There are limited studies supporting the use of…
Arthrodesis vs Arthroplasty in Thumb CMC OA
Piacenza A, Vittonetto D, Rossello MI, Testa M. Arthrodesis Versus Arthroplasty in Thumb Carpometacarpal Osteoarthritis: Impact on Maximal Voluntary Force, Endurance, and Accuracy of Pinch. J Hand Surg Am. 2021 May 24:S0363-5023(21)00199-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.03.023. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34045112. The Skinny: This was a retrospective study based on a convenience sample of individuals who…
THE SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY OF ULTRASOUND FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME: A META-ANALYSIS
Fowler, J. R., Gaughan J. P., & Ilyas, A.M. (2011). The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research, 469(4), 1089-1094. The Skinny –The authors sought out to determine the sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound therapy for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome using…
IFC vs TENS: Electrical Stimulation for Pain and Swelling
In this article we’re looking at the difference between Inferential Current versus Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation (IFC vs TENS). Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation (TENS) TENS variations are often described by their technical characteristics: high frequency, low intensity (conventional TENS) or low frequency, high intensity (acupuncture-like TENS, AL-TENS) (Walsh et al., 2009). How TENS Addresses Pain:…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.





Thank you so much! I always enjoy your informative blogs and have learned a great deal. Your effort is very much appreciated!!!