Peripheral nerve injury: A hand therapist’s assessment of sensory return.
Filed under Evaluation
Sensory return after a hand injury specifically a peripheral nerve injury
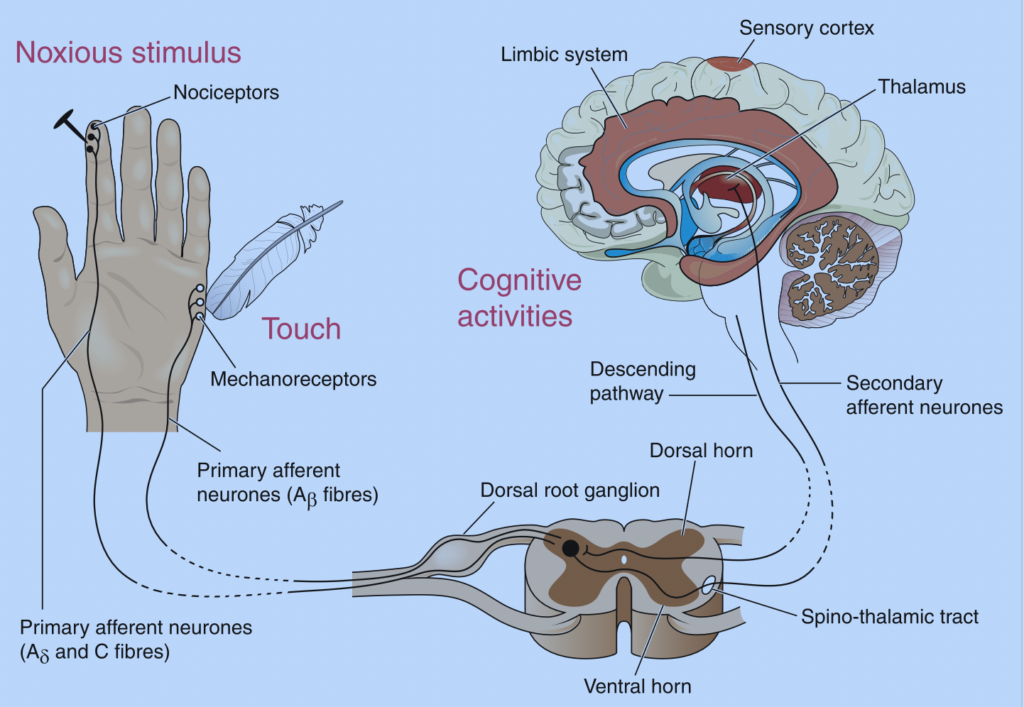
After a peripheral nerve injury, there are often times impairments in sensory function and/or motor function. The rate of recovery varies based on the degree of injury, the overall health of the patient, and the patient’s age.
After an injury, it is important to be able to accurately assess the motor and sensory function. This can give insight into the severity of the injury and also give therapists a better idea of recovery. If there is motor involvement performing manual muscle testing is key. With sensory impairments, it is important to know the order of sensory return. Hence the reason for this paper.
Order of Sensory Recovery
1.) Pain
2.) Temperature
3.) Vibration 30 Hz
4.) Moving Touch
5.) Constant Touch
6.) Vibration 256 Hz
7.) Touch Localization
8.) Two-Point Touch
9.) Stereognosis
1.) Pain is the first to return. This is our body’s way of letting us know when something is not right. When we sense pain we often modify what task is being performed or rest to avoid further injury. Pain is perceived through the nociceptor of the sensory system.
Pain can be tested clinically using a sharp/dull assessment. This assessment can be performed using a neurological pin, a safety pin, or a paper clip unfolded. You will take the chosen instrument and use the sharp and dull edge to press it on the patient’s skin. They will report if they are feeling sharp vs dull pain. It is important to not apply these stimuli too close together to avoid the summation of sensory responses.
2.) Temperature is second to return. This is how we determine if an object is too hot or cold to touch. Being able to detect hot vs cold is important in preventing burns. If a patient is unable to detect hot or cold, it is important to provide education on preventing injuries.
Testing for hot and cold after a peripheral nerve injury involves the utilization of test tubes. One tube is filled with hot water (40-45 degrees Celsius) and the other with cold water (5 to 15 degrees Celsius). The patient is asked to verbalize if they feel hot vs cold after each stimulus application.

3.) Vibration 30 Hz. It is very difficult to assess 30 Hz of vibration as it is a low-frequency vibration. This level of vibration is detected with the Meissner’s Corpuscles. You can use a tuning fork to determine if they feel the vibration. A tuning fork is around 128 Hz. Not exactly an accurate measurement.
4.) Moving touch can be tested by using a cotton ball and gently stroking along the test area. The patient is asked to identify when they feel the stimulus. Moving touch is easier to detect than constant touch and touch localization.
5.) Constant touch can be tested by using the tip of your finger and applying pressure. The patient is asked to identify when they feel the stimuli. Keep in mind finding the location at this point is not needed.
6.) Vibration 256 Hz. This is a much higher frequency vibration and the Pacinian Corpuscles are the sensory receptors used to identify this stimulus. Similar to the 30 Hz there are no accurate stimuli to test Vibration of 256 Hz.
7.) Touch Localization. Touch localization is next to return. This is tested by applying light touch and asking the patient to identify the location of the touch.
8.) Two-Point Touch. This is the ability of an individual to perceive two points of pressure when applied to the skin at the same time. Typically a circular two-point discriminator is used to test the skin. Initially, the tips are spread apart and the distance between the two tips gets smaller until only one point is perceived.
9.) Stereognosis. This is the ability to determine what an object is through touch. Limitations in stereognosis can be found after a peripheral nerve injury. It is typically the last to return. To test stereognosis have the patient’s vision occluded and ask them to identify common objects. Examples of common objects include a key, bolt, coins, and/or a paper clip.
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
7 Tips to Improve your Chances of Passing the Certified Hand Therapy Exam
There are several predictors for success when taking Standardized Exams. One key component is self-regulated learning and the application of study strategies. Studies have shown if Certified Hand Therapy Exam takers cannot self-regulate or monitor their knowledge, they will demonstrate poor exam performance. Self-regulation is how learners gain knowledge while monitoring and reflecting on their…
Read MoreDRUJ Instability and Hand Therapy Interventions
DRUJ Instability and Hand Therapy Interventions The distal radial ulnar joint (DRUJ) is the joint consisting of the distal radius and ulna which is held together by the ligamentous structure known as the TFC. DRUJ instability can be acute or chronic in nature. An acute injury is usually addressed by placing the patient in a…
Read MoreTitle: Understanding De Quervain’s Pathology: A Comprehensive Exploration of Special Tests
Understanding De Quervain’s Pathology: A Comprehensive Exploration of Special Tests By: Miranda Materi De Quervain’s and Special Tests De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist, causing pain and discomfort. These tendons include Abductor Pollicis Longus (APL) and Extensor Pollicis Brevis as they pass through…
Read MoreSign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




This is so well laid out. Thank you. Loving the graphics too.
Thank you!