How to Strengthen the Intrinsics with Puttycise Tools:
Filed under Treatments
I’m always looking for ways to strengthen the hand intrinsics. It is easy to overlook the importance of these small but mighty muscles. They are very important to performing functional grasps patterns. They can become weak in a short period of time due to their small size.
So, How does it work?!
The Basics – I usually start with a large 5 pound blob of yellow or tan hand therapy putty because this is the easiest and softest.
“Functional grasp patters require the use of the intrinsics.”
Special Rules – To keep the patient from cheating and to meet the purpose of the task we have a few special rules.
- Make sure the patient’s shoulder is relaxed! We do not want to create shoulder problems!
- Check to make sure there is no compensation of the long flexors and extensors.
- The most important part of these exercises is TECHNIQUE
Make it fit – This task is scalable and can be adjusted by using different puttys. Also it can be modified by how deep you dig the putty tools into the hand strengthening putty.
Now lets get to work!
Using the small cylinder knob, place it between digits 2 and 3. While holding the knob tight between the digits turn the knob in the putty. Repeat the same step above and rotate the knob to in between digits 3 and 4 and than digits 4 and 5.
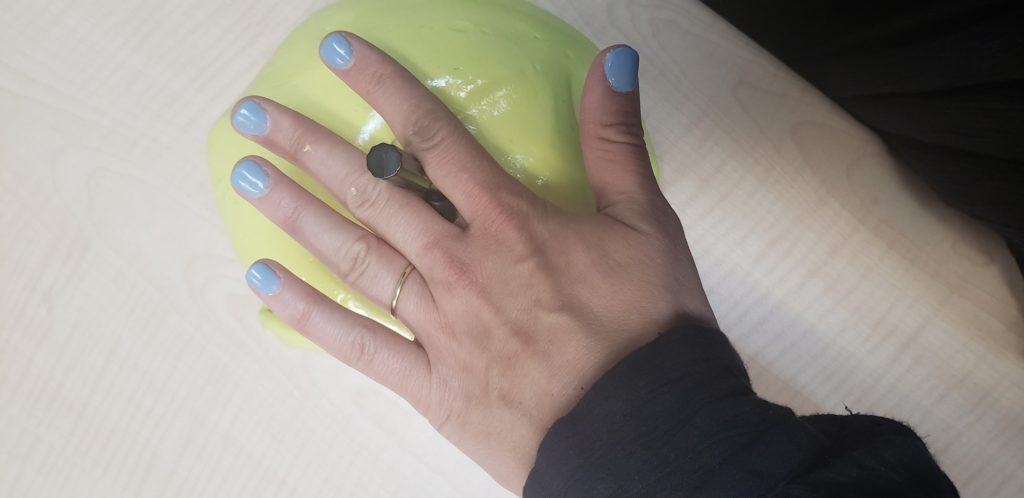

Next, push the t-end of the putty tool into the putty. Hold the hand in the intrinsic plus position and practice turning the knob.
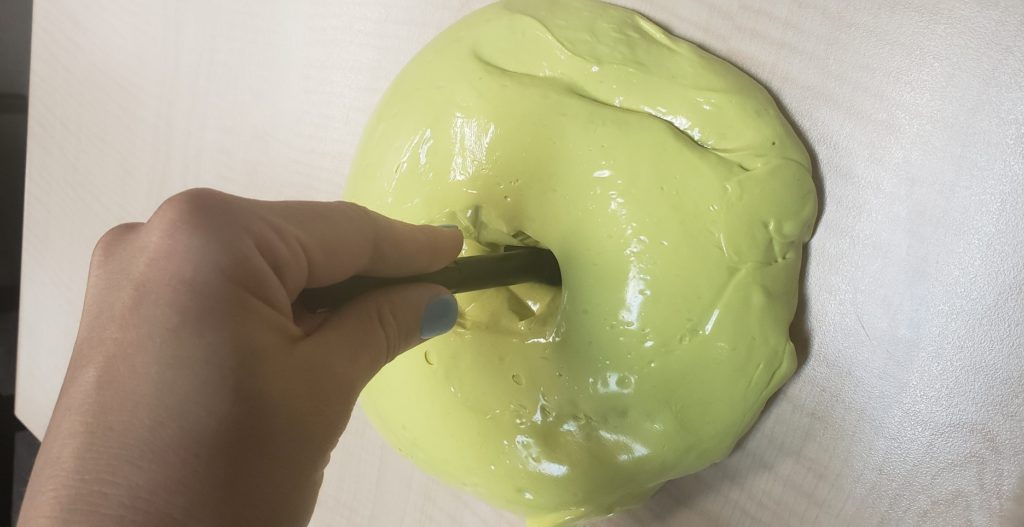

Lastly, Intrinsic Pull. Place one side of the key tool into the putty, hold tool between any two digits and pull through putty.
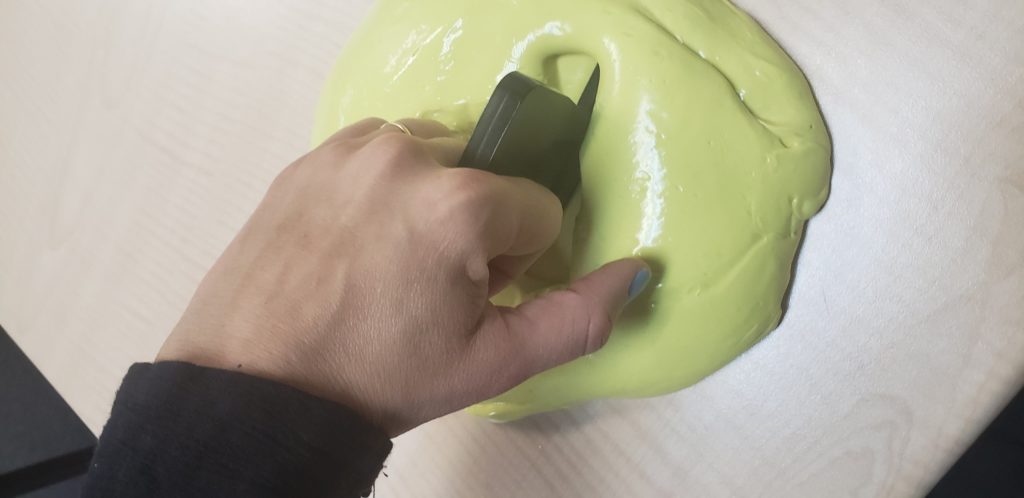

Warning – Make sure the patient removes their watch or bracelet along with making sure their phones do not get near the putty. The putty tends to stick to rubbery surfaces and can be very difficulty to remove.
If you don’t have Puttycise tools you can make your own out of scrap splinting material.
4 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
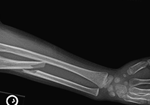
Hand Therapy: Conservative Management of Pediatric Monteggia Fractures
Conservative Management of Pediatric Monteggia Fractures Monteggia fractures in children comprise approximately 2% of pediatric elbow fractures and involve a fracture of the proximal ulna with dislocation of the radial head (Fig. 1). The primary concern of Monteggia fractures includes the treatment (monteggia fracture treatment pediatric) and relocation of the radial head, because if left…
Hand Contractures from Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
What is Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita?Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita (AMC) is a rare congenital condition that is characterized byan individual being born with multiple joint contractures, involving two or more areas of the body(Khurana et al., 2024). AMC is a general term that describes over 400 different medicalconditions that involve joint contractures, instead of just describing one…
Ultrasound use for reducing pain: Does it work?
Ilter, L., Dilek, B., Batmaz, I., Ulu, M.A., Sariyildiz, M.A., Nas, K., & Cevik, R. (2015). Efficacy of pulsed and continuous therapeutic ultrasound in myofascial pain syndrome: A randomized controlled study. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 94(7), 547-554. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0000000000000210 Review by: Megan Prather The Skinny- Ultrasound hand therapy – ultrasound has been determined…
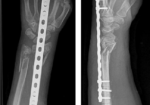
Outcomes of Dorsal Bridging Plates
Outcomes of Dorsal Bridging Plates Fares, A. B., Childs, B. R., Polmear, M. M., Clark, D. M., Nesti, L. J., & Dunn, J. C. (2021). Dorsal Bridge Plate for Distal Radius Fractures: A Systematic Review. The Journal of Hand Surgery. https://doi-org.methodistlibrary.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2020.11.026 The Skinny Distal radius fractures (DRF) are a common injury that we see in…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




Hey! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if
that would be okay. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look forward to
new posts.
We do the majority of our posting @handtherapyacademy on Instagram
Hello dear Miranda and dear Josh, I am from a city in Germany, I enjoy your information and my work in the hand therapy. Have you already recommended to colleagues on. Please keep it up, it’s great to read your posts.
I am looking forward to exercises for patients with finger and wrist fractures as well as anatomy and biomechanics. Especially the latter, I do not find much on the Internet. Many thanks for that! Kathrin Sauer from germany