Splinting and Stretch Protocol for Pediatric Trigger Thumb
Filed under Treatments
Tan, A. C., Lam, K. S., & Lee, E. H. (2002). The Treatment Outcome of Trigger Thumb in Children. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics B, 11(3), 256-259.
The Skinny:
Pediatric trigger thumb is a “relatively uncommon” condition of unknown origins. Studies have indicated that spontaneous recovery of trigger thumb is around 25-40%, and chances increase with age. Meanwhile, implementation of conservative treatment splint therapy, in conjunction with passive stretch programs (pediatric trigger thumb exercises), have shown successful recovery rate as great as 89%.
This review analyzes the success of nighttime/naptime only thumb extension orthotic wear in conjunction with a passive stretch exercises protocol (pediatric trigger finger exercises).
In the Weeds:
115 patients with noted flexion contracture deformity or present triggering/snapping were reviewed. Boys and girls were equally affected, as were left and right thumbs. 23 children had bilateral thumb involvement.
59 children, with an average age of 26.5 months, were treated surgically with A1 pulley release. 56 children, with an average age of 19 months, were treated conservatively with splint therapy.
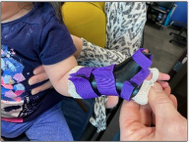
Splint therapy consisted of nighttime/naptime wear of a thumb extension orthotic (see image) with regular clinic sessions for passive stretch to the thumb, and splint modifications to increase thumb/IP extension (pediatric trigger thumb splint).
Bringing It Home:
Conservative treatment showed an overall success rate of 66%. The success rate decreased with increasing age: from 89% in the under 1 year-old age group to 50% in the over 3 year-old old age group.
Of the 56 patients having conservative treatment, 31 had splint therapy and 25 had passive stretch only. Splint therapy resulted in 77% success rate compared to 52% with the stretch-only group, demonstrating that use of orthotic in conjunction with passive stretch shows the best recovery. Overall, 76% of patients were successfully treated conservatively within 6 months.
For those patients who underwent surgery, either initially or after failed conservative treatment, 1.4% had a recurrence of triggering, and 2.8% had subsequent wound infection requiring treatment with antibiotics.
Limitations: This article asserts that trigger thumb in pediatrics is most likely attributed to acquired injury rather than a congenital anomaly, as none of the participants presented with trigger thumb prior to
six months of age. However, this overlooks the concept that indwelling thumb is developmentally appropriate up through 5 months of age, so observation of thumb IP flexion or thumb flexion prior to
this age would not indicate referral, even if trigger thumb may be co-occurring.
The article does not directly compare the success rates of surgical versus conservative treatment methods. It explains the success rates of conservative treatments while only stating the failure rates of
surgical intervention, which skews the statistics against each other.
More To Read
A Review on the Conservative Management of Trigger Finger
Lunsford, D., Valdes, K., & Hengy, S. (2017). Conservative management of trigger finger: A systematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy, 32(2), 212-221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2017.10.016 The Skinny The main purpose of the literature review was to determine the efficacy of conservative management of trigger finger (TF) through the use of an orthosis in addition to therapy. The review…
Hand therapy intervention activities for Chemo-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN)
Blog Post Written By: Rita Steffes Patients with CIPN may present with symptoms that include numbness, tingling, hypersensitivity to cold, loss of tactile or vibration sensitivity, decreased balance, and shooting burning pain in their hands These symptoms make it difficult for oncology patients to participate in all activities of daily living with dressing, meal preparation,…
How to Improve Fine Motor Translation Skills
By: Josh MacDonald The Basics – I lay a pile of small objects on the table and an open container for the client to put them into. What object I use depends on the client’s level. We’ll get to that later. Then, they use a 2-point pincer grasp to pick up one and shift it…
THE SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY OF ULTRASOUND FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME: A META-ANALYSIS
Fowler, J. R., Gaughan J. P., & Ilyas, A.M. (2011). The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research, 469(4), 1089-1094. The Skinny –The authors sought out to determine the sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound therapy for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome using…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.