Which is better: Splinting the MCP or PIP joint when managing Trigger Finger?
Filed under Orthoses, Treatments
Teo, S. H., Ng D. C., Wong, Y.K.(2018). Effectiveness of proximal interphalangeal joint blocking orthosis vs metacarpophalangeal joint blocking orthosis in trigger digit: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Hand Therapy, 1-7.
The Skinny- This study compared PIP joint immobilization via an Oval-8TM with a custom MCP blocking trigger finger orthosis treatment.
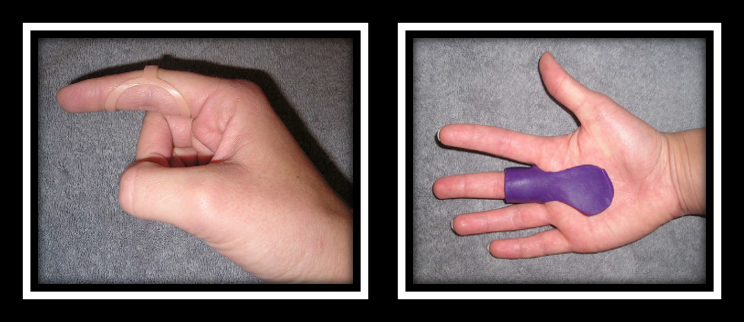
In the Weeds – Patient (n=35) with Trigger Finger (n=43) were analyzed. Twenty-three patients were allocated to the PIP joint splinting group and 20 patients were in the MCP splinting group. Patients wore the orthosis for eight weeks – these were MCP splint for trigger finger, MCP blocking splint and pip joint splint.
Pain reduction was observed in both groups, but pain reduction was greater with PIP joint splinting compared to the MCP joint splinting group. There was only significant improvement in QuickDASH for the PIP splinting Group. Patients wore the pip joint splint significantly longer during the day compared to the MCP splinting group, most likely due to improved comfort.
Bringing it Home- Findings suggests both orthoses are effective in reducing QuickDASH scores, reducing pain and improving overall trigger finger symptoms based on Green’s Classification. However, the pip joint immobilization splint was better for improved function and improved compliance.
Rationale for rating. Small sample size. All patients with comorbidities were excluded limiting the generalizability of finding. Immobilizing the PIP joint compared to the MCP allows more function and improved compliance. When immobilizing the MCP you limit intrinsic grasp which is a necessity for function. The authors recommend wearing the orthosis for a 4 week duration for 24 hours in order to reduce triggering symptoms followed by night-time splint wear for another 3-4 weeks.
10 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
THE SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY OF ULTRASOUND FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME: A META-ANALYSIS
Fowler, J. R., Gaughan J. P., & Ilyas, A.M. (2011). The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research, 469(4), 1089-1094. The Skinny –The authors sought out to determine the sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound therapy for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome using…
Orthotic Options for Hand Burns
By: Sophia Grimm Hand burns can be very challenging to treat, and successful rehabilitation begins early after acute injury. Following a burn injury, scar contractures are the primary reason for the deformity of the hand. Therefore, proper orthotic intervention is key to preventing joint and ligament contractures (Kelly, Berenz & Williams, 2019). Splinting goals following…
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM hand)
By: Amalia Garcia Introduction After completing three weeks of my Level II hand therapy rotation, I have seen a wide variety of common upper extremity injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome, distal radius fractures, mallet finger, flexor tendon lacerations, arthritis, and more. One condition that stood out to me was one that I hadn’t heard…
Do you know the difference between an Electromyography (EMG) and a Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) Study?
Do you know the difference between EMG and NCV (an Electromyography and a Nerve Conduction Velocity Study? The term nerve test is usually a broad term that typically indicates both an Electromyography (EMG) and a Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) study (EMG vs NCV). An EMG looks at the electrical signals your muscle makes when at…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




This is great! Keep them coming!
really interesting- thanks
We’re glad you liked it. We will keep them coming.
Love this!!! Thank you.
Glad you liked it!
Thanks for sharing !
What about PIP range of motion ?
Typically we instruct the patient with prom and to avoid active if it is causing the triggering to occur.
Thanks for sharing!
Important to know.
This is great – curious if there was a time frame of symptoms present for inclusion criteria and or for splinting to be effective? ie if the patient had triggering for less than 3 months splinting was found to be effective; or were patients who had symptoms for longer than x-amount of weeks/months were not included, etc etc? I have always been under the impression if symptoms are too severe/present for more than 4 weeks cortisone injection is kind of the gold standard as splinting is less effective at that point? Thank you!
Yes, the longer the condition goes on the more difficult it is to treat. From personal experience, I have had patients resolve their symptoms for trigger fingers that have been going on for 6 months