Mechanism of Interneural Edema in Carpal and Cubital Tunnel
Filed under Diagnoses
Mechanism of Interneural Edema
Over the last few weeks I have been learning about ultrasonic imaging and carpal tunnel syndrome. When reviewing carpal tunnel syndrome, I learned that intraneural edema is a common sign of compression injuries such as carpal tunnel and cubital tunnel. There are numerous causes of carpal tunnel syndrome, and every scenario ends with the reduction of available space within the carpal tunnel and the inevitable compression on the median nerve (carpal tunnel edema). What I did not know was that chronic compression on the nerve can disrupt and open the blood nerve barrier around the perineurial layer. This allows for blood to flow freely into the nerve causing swelling or interneural edema. Since the nervous system lacks lymphatic drainage in the endoneural space, swelling inevitably increases pressure and disrupts the flow of blood to the nerve resulting in a metabolic conduction block (Cooper, 2014). One animal study found that an increase in pressure as little as 30 grams of force (about the weight of an average lightbulb) over the course of 1 hour was enough to disrupt the blood nerve barrier around the median nerve and cause diffusion (Kobayashi et al., 2005).
Normal Nerve No Diffusion
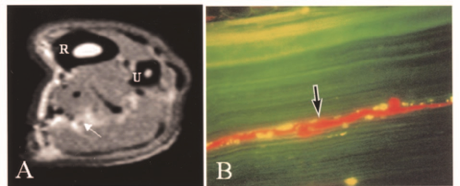
Nerve 30 Grams of Force with Diffusion
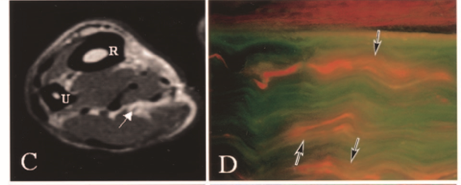
Nerve 90 Grams of Force Severe Diffusion
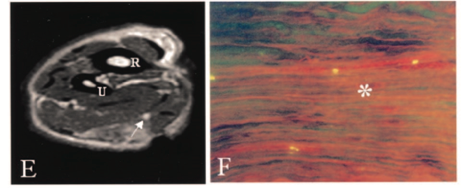
Chronic compression and decreased blood flow lead to impairment in nerve conduction. One source states that functional deficits are seen sequentially in the following order: motor, proprioception, touch, temperature, pain, and then sympathetic function (Cooper, 2014). Therapeutic activities such as nerve gliding exercises are hypothesized to increase nerve mobility and release the nerve from the sight of compression. Additionally, surgical decompression can help to alleviate symptoms, but the timeline for neural repair is largely based on the severity of nerve damage that has occurred. As neural edema subsides and blood flow to the nerve improves, the nerve begins to repair itself as long as the endoneurial tubes are intact. Patients are expected to regain sensation in the reverse order that they were initially lost (pain, temperature, proprioception).
Cooper, C. (20014). Fundamentals of hand therapy: Clinical reasoning and treatment guidelines for common diagnoses of the upper extremity [Second Edition]. Elsevier Mosby
Kobayashi, S., Meir, A., Baba, H., Uchida, K., and Hayakawa, K. (2005). Imaging of intraneural edema by using gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging: Experimental compression injury
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Peripheral nerve injury: A hand therapist’s assessment of sensory return.
Sensory return after a hand injury specifically a peripheral nerve injury After a peripheral nerve injury, there are often times impairments in sensory function and/or motor function. The rate of recovery varies based on the degree of injury, the overall health of the patient, and the patient’s age. After an injury, it is important…
Wound Healing Complications in Diabetic Patients who have undergone a Carpal Tunnel or Trigger Finger Release
By: Amalia Garcia Gundlach, B. K., Robbins, C. B., Lawton, J. N., & Lien, J. R. (2021). Wound Healing Complications in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Carpal Tunnel and Trigger Finger Releases: A Retrospective Cohort Study. The Journal of Hand Surgery, S0363502321003014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.05.009 The Skinny – carpal tunnel and diabetes In general, individuals with diabetes are more…
Early Mobilization After Volar Locking Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Radius Fractures in Older Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
By: Rachel Reed Sørensen, T. J., Ohrt-Nissen, S., Ardensø, K. V., Laier, G. H., & Mallet, S. K. (2020). Early Mobilization After Volar Locking Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Radial Fractures in Older Patients-A Randomized Controlled Trial. The Journal of hand surgery, S0363-5023(20)30276-8. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2020.05.009 The Skinny: The purpose of this randomized controlled trial was…
Splinting Options for Stiff Finger Joints
Following an injury to the proximal interphalangeal joint, there is often a loss of range of motion, typically in both the flexion and extension planes. Therefore, we have compiled a list of helpful splinting options for stiff finger joints. To Improve PIP Joint Flexion Flexion Wrap with Elastic Tape (Coban): This is a very easy…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.





The inter neural edema is fascinating.
Yes is is very interesting! I agree